Article Contents:
From an organizational perspective, problem-solving competency refers to the collective ability of individuals or teams within the organization to effectively identify, analyze, and resolve problems that arise during business operations.
This competency is essential for maintaining efficiency, fostering innovation, and achieving the organization’s strategic objectives.
In this article, I have given my framework for assessing small organizational problem-solving maturity at any time. This will help you assess your organization’s current problem-solving maturity level.
Once you are aware of the current state, you can make an effort to take it to the next level of competency in a structured way, as is done in growth-oriented organizations.
Assess your organizational problem solving maturity
To assess the organizational problem-solving maturity level, you first need to understand the levels of problem-solving maturity.
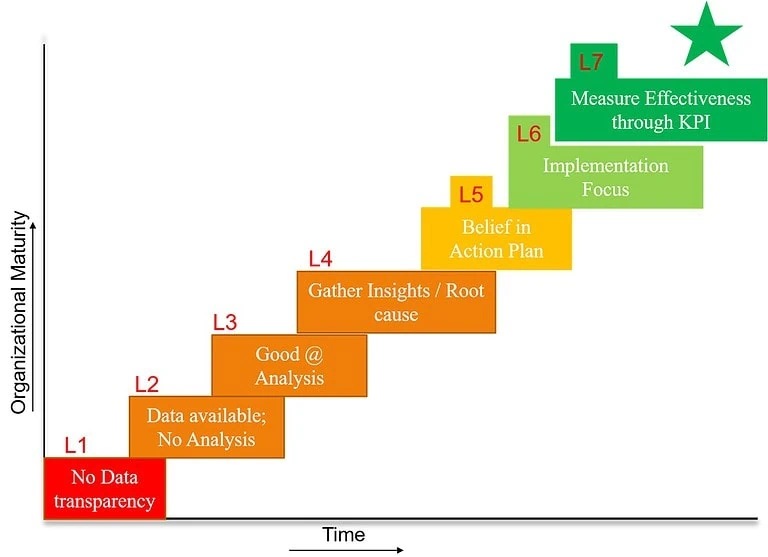
As the organization progresses, it will advance through the 7 stages of maturity outlined below.
Level 1 maturity: No systematic data collection
Level 2 maturity: Data available, but no structured analysis of data
Level 3 maturity: Good at Analysis
Level 4 maturity: Gather insights from analysis and good at finding root causes
Level 5 maturity: Belief in Holistic Action Plan; Focus on Solutions Approach
Level 6 maturity: Implementation focus across the organization
Level 7 maturity: Track the implementation effectiveness through metrics, say KPI
Below is a visual representation of organizational maturity level with reference to time.
The ultimate maturity is LEVEL 7, in which the organization is driven by structured problem-solving methods and validated by key performance indicators rather than opinions or emotional drives.
Now, you hold on for a few minutes and assess your organizational capability.
In some organizations, generally operations team may have higher level of maturity, whereas other functions stand at lowe level of maturity.
My suggestion is that as the head of the organization, you have to look at the whole organization and assess its level of maturity. That holistic assessment will help you understand your organizational capability better than functional level capability.
Let us understand each maturity level with examples and how the leadership team can drive the organizational maturity towards level 7.
Problem solving maturity Level 1: No Data Transparency
Level 1: No Data Availability
Current State: The organization lacks systematic data collection methods, hindering its ability to understand and address problems effectively.
Example:
A small manufacturing company experiences product quality issues but lacks a system to track production data or customer feedback.
A retailing business does not collect data on customer visits and lost sales data.
A manufacturing unit is unable to meet the delivery commitments but lacks the data to explain why it is failing.
Solution Approach:
- Implement basic data collection mechanisms like quality inspection records and customer complaint tracking systems.
- Use technology to count the number of customer footfall and sales conversion data.
- Train employees on data collection processes and emphasize capturing relevant information.
Problem solving maturity Level 2: Data Available; No Analysis
Level 2: Availability of Data without analysis
Current State: Data collection exits, bit is sporadic and not utilized effectively for problem-solving purposes.
Example:
The manufacturing company sporadically records production losses due to various reasons in production records, but the data remains underutilized, sometimes not shared with anyone.
There is no further analysis of the loss data.
The manufacturing company occasionally reviews production data but lacks a systematic analysis framework to identify the root causes of quality issues.
Solution Approach:
- Centralize data collection processes and establish standardized data capture procedures.
- Invest in data management tools or software to efficiently organize and analyze collected data.
- Develop structured analysis frameworks, such as Pareto analysis or root cause analysis, to systematically examine data and identify trends or patterns.
- Train employees on data analysis techniques and encourage cross-functional collaboration in problem-solving efforts.
Problem solving maturity Level 3: Good at Analysis
Level 3: Good Analysis of data
Current State: Data is available, and people are trained to analyze using data analytics tools.
Example:
In some organizations, the software provides data analysis for decision-making, but people do not review the analysis or conclusions.
A manufacturing unit has automated the collection of equipment effectiveness data through a sensor-based system.
At the end of the day, the centralized computer system collects the data, analyses it, and presents it to the team in a simple form. However, people do not get an insight into the data analysis.
Solution Approach:
- The leadership team should encourage the team to review the data summary daily/weekly through cross-functional review forums.
Problem solving maturity Level 4:Gather Insights / Good at Finding Root cause
Level 4: Gaining Insight from Analysis
Current State: The organization starts to derive insights from data analysis but lacks consistency in applying these insights across problem-solving efforts.
Example: Current State: After analyzing production data, the manufacturing company identifies a correlation between machine downtime and quality defects but struggles to implement preventive maintenance measures consistently.
Solution Approach:
- Foster a culture of data-driven decision-making by emphasizing the importance of applying insights from analysis to drive improvement initiatives.
- Establish cross-functional teams to translate insights into actionable solutions and ensure consistent implementation across the organization.
Problem solving maturity Level 5: Belief in Holistic Action Plan
Level 5: Converging into Solutions Approach
Current State: Solutions are being explored, but there is a need for a more comprehensive approach aligned with organizational goals.
Example: Current State: The manufacturing company implements ad-hoc solutions to address quality issues but lacks a cohesive strategy to improve overall production efficiency.
Solution Approach:
- Develop structured problem-solving methodologies, such as DMAIC (Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, Control) or PDCA (Plan, Do, Check, Act), to guide solution development and implementation.
- Align problem-solving efforts with organizational goals and priorities to ensure solutions contribute to long-term success.
Problem solving maturity Level 6: Implementation Focus
Level 6: Implementation Focus
Current State: Solutions are identified but may lack consistency or thorough follow-through in implementation.
Example: Current State: The manufacturing company introduces new quality control measures but struggles to ensure consistent adherence across shifts or departments.
Solution Approach:
- Strengthen project management capabilities to oversee solution implementation, including setting clear objectives, timelines, and responsibilities.
- Establish mechanisms for ongoing monitoring and feedback to track progress and address implementation challenges proactively.
Problem solving maturity Level 7: Measure Effectiveness through KPI
Level 7: Track Performance Through Metrics
Current State: Solutions are implemented, but there is limited focus on tracking performance metrics to assess effectiveness.
Example: Current State: The manufacturing company implements quality improvement initiatives but does not track metrics such as defect rates or customer satisfaction scores.
Solution Approach:
- Define key performance indicators (KPIs) to measure the impact of implemented solutions and track progress towards organizational goals.
- Implement regular performance reviews and data-driven decision-making processes to ensure continuous improvement and sustainment of gains.
How leader can drive problem solving maturity or capabilities in the organization ?
One of the aspiration for most of the small business owner is to inculcate the culture of problem solving among the people so that they can focus on business growth and strategic thinking.But In reality, the day to day priorities do not allow them to bring the culture of problem solving.
Before getting into the methods of driving problem solving competency in the organization , let us understand the root causes for not able to create the culture.
Root causes for not able to create the problem-solving culture
Some of the factors or behaviors of senior leadership team do not allow the people to get into the structured problem-solving mindset.
1. Not realizing the problem or trend in the business
2. No structured, authentic data from source
3. Culture of jumping to quick solutions, once problem is identified
4. Managers are conditioned to give quick solutions rather than probing
5. Busy in day to day firefighting and “somehow” resolving issues
6. Hesitate to conclude the solutions approach or options
7. No facilitation on arriving solutions approach
8. No risk taking or rewarding risk takers
How can leaders drive to create problem-solving mindset and culture inside the organization
Obviously, the people have to be given education exposure to different problem-solving methodologies, tools, and techniques.
Assuming that education or awareness part is taken care, the senior leadership team has more responsibility to create a conducive environment or demonstrate consistent behavior towards solving problems.
The following solutions approaches are recommended
1. Building an environment to collect authentic, consistent data from source
2. Encouraging discussions based on facts rather than opinions.
3. Creating a routine forum or reviews to discuss the problems and solutions approach
4. Encouraging open debate and idea generation by keeping ego aside
5. Allowing others to talk and listen more for insights
6. Encouraging people to take risk and experiment with solutions approach
7. Differentiating and recognizing problem solvers.
Summary
In today’s competitive environment, one of the differentiators and competitive edge for the organization is to create more problem solvers and to create a culture of problem-solving maturity or competency across levels and functions!
And Leaders play a major role in creating a conducive environment for developing problem solving competency.